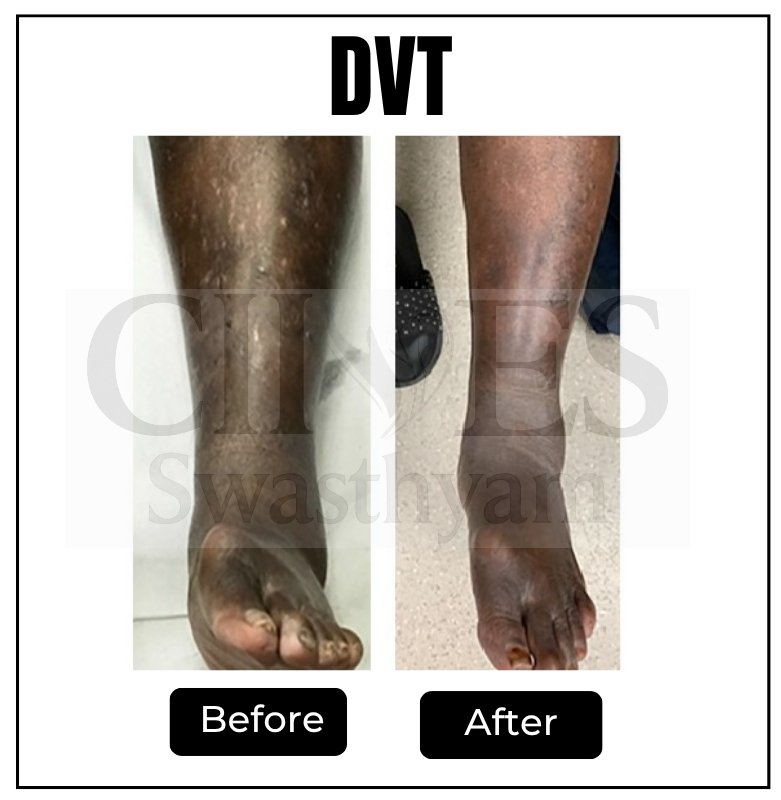
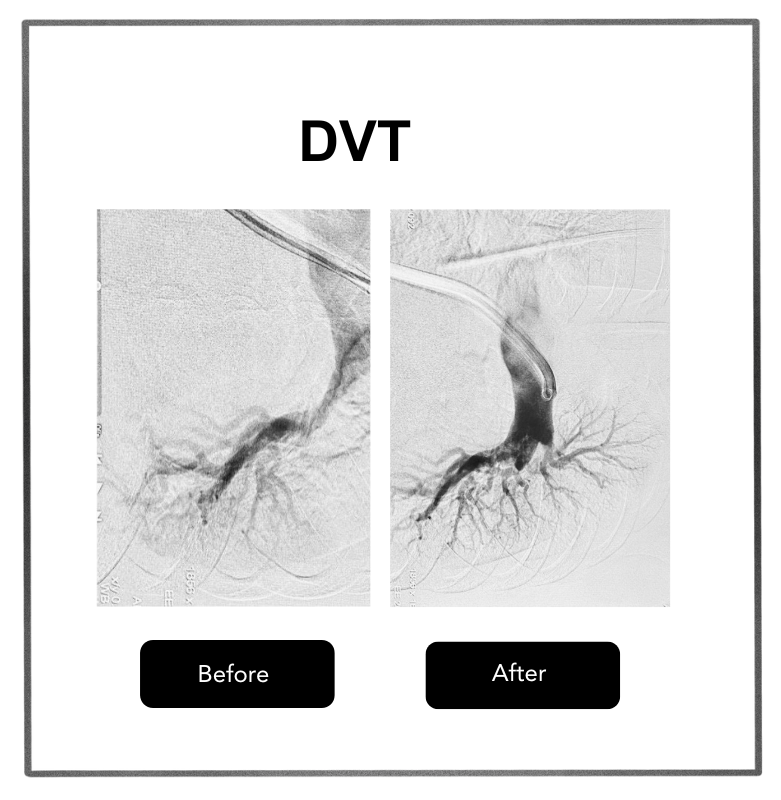
These signs, often dismissed as fatigue or ageing might indicate a clot in leg or Acute DVT.
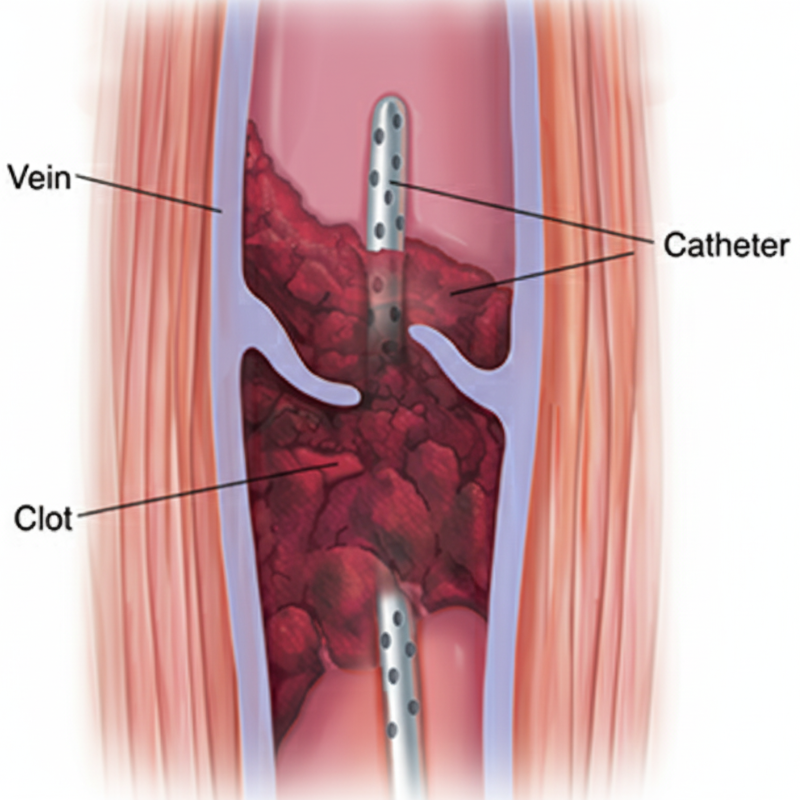
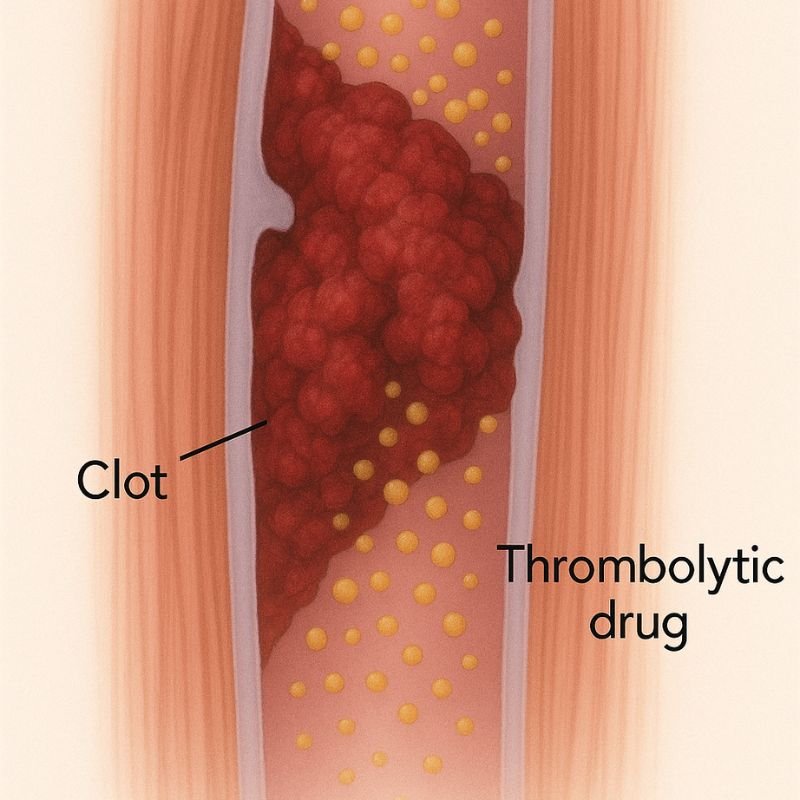
Deep Vein Thrombosis or Acute DVT is the sudden formation of a blood clot in the deep veins, usually in the legs. This clot can partially or completely block blood flow, leading to severe pain, swelling, & dangerous complications.
If untreated, the clot can dislodge and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism (PE): a medical emergency that can be fatal!
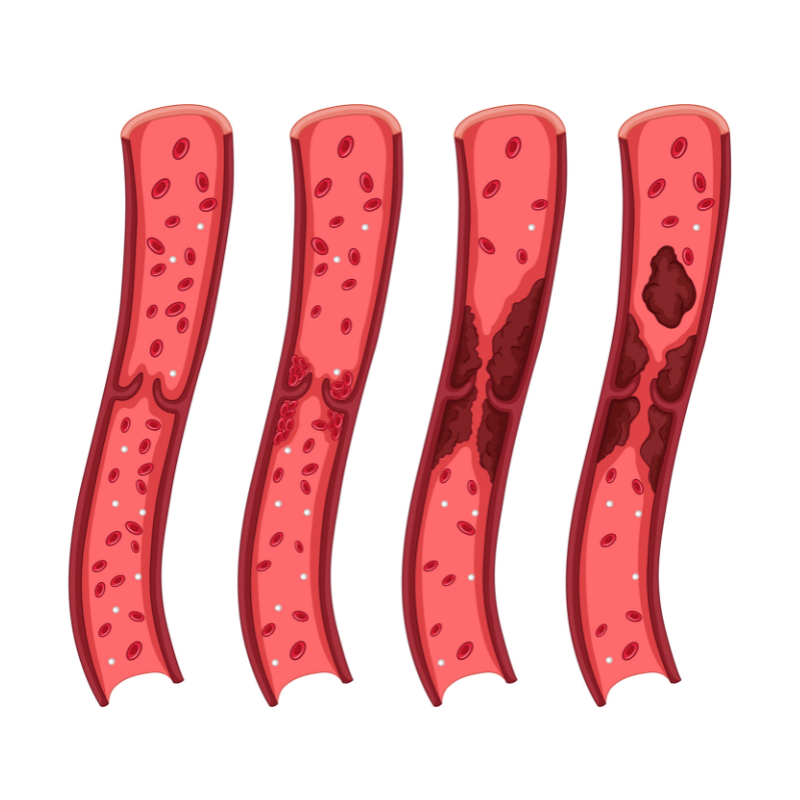
Spotting DVT early is crucial for preventing serious complications. Common DVT symptoms include:


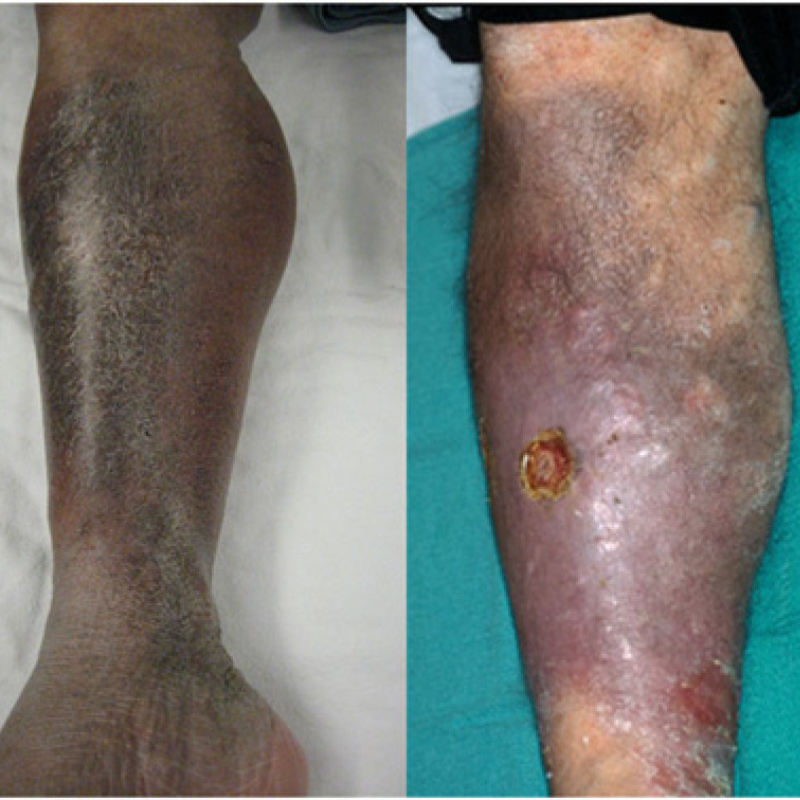
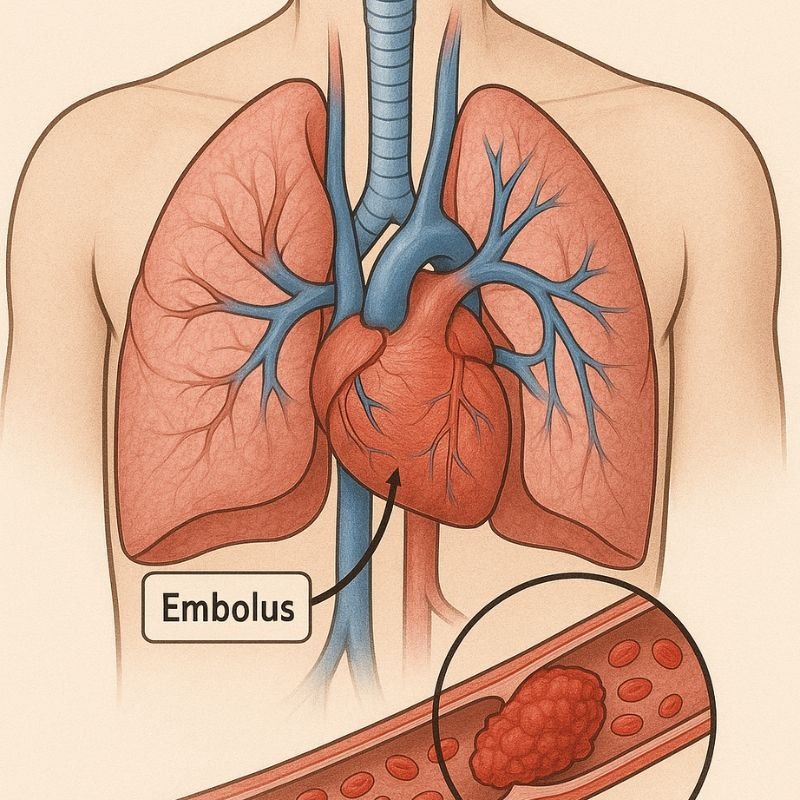
If a blood clot dislodges and travels to the lungs, it can block a lung artery, cutting off blood flow and oxygen exchange. This leads to the following signs: