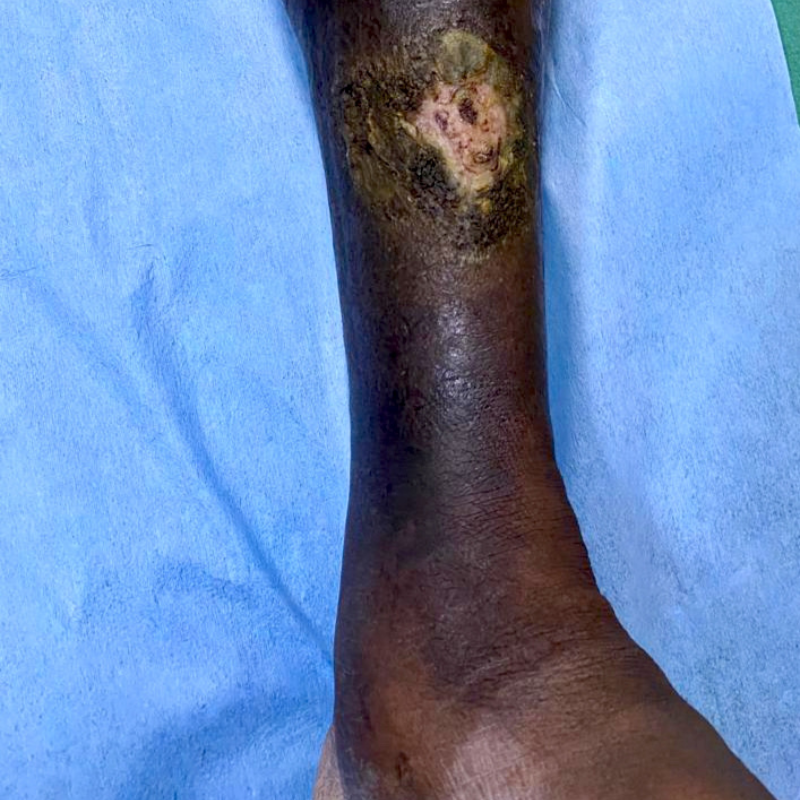
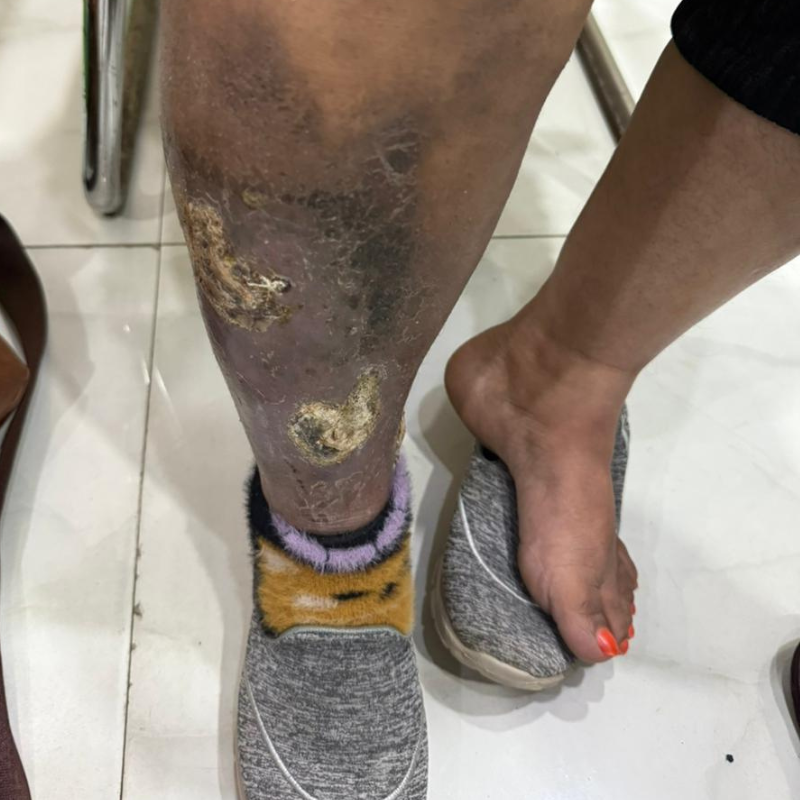
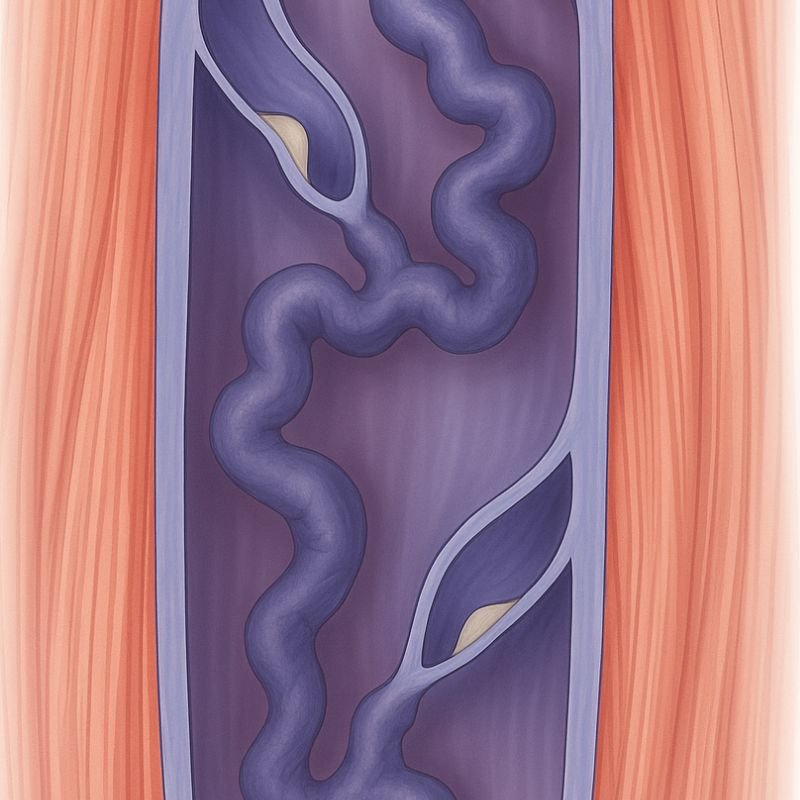
Clots in the deep veins (DVT) that are not resolved within 1–2 months may become chronic, leaving the vein partially blocked or scarred. Even when the DVT is treated, the damage to the vein’s valves is already done.
Chronic Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot in the deep veins of the leg remains undetected or does not completely dissolve.
Over time, the clot becomes firm and fibrotic, leaving the vein partially blocked or permanently narrowed.
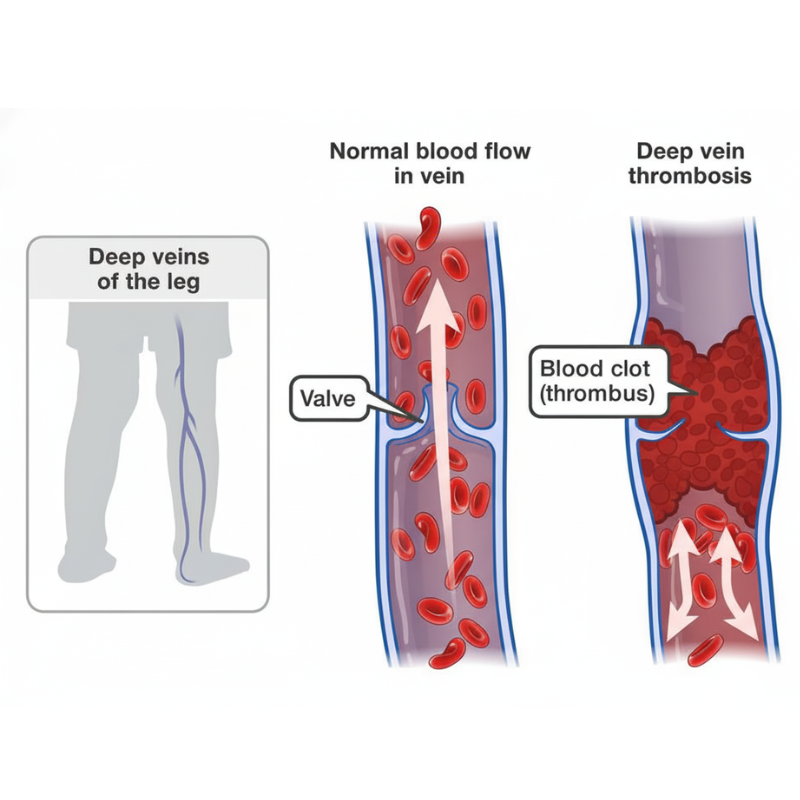
Put simply:
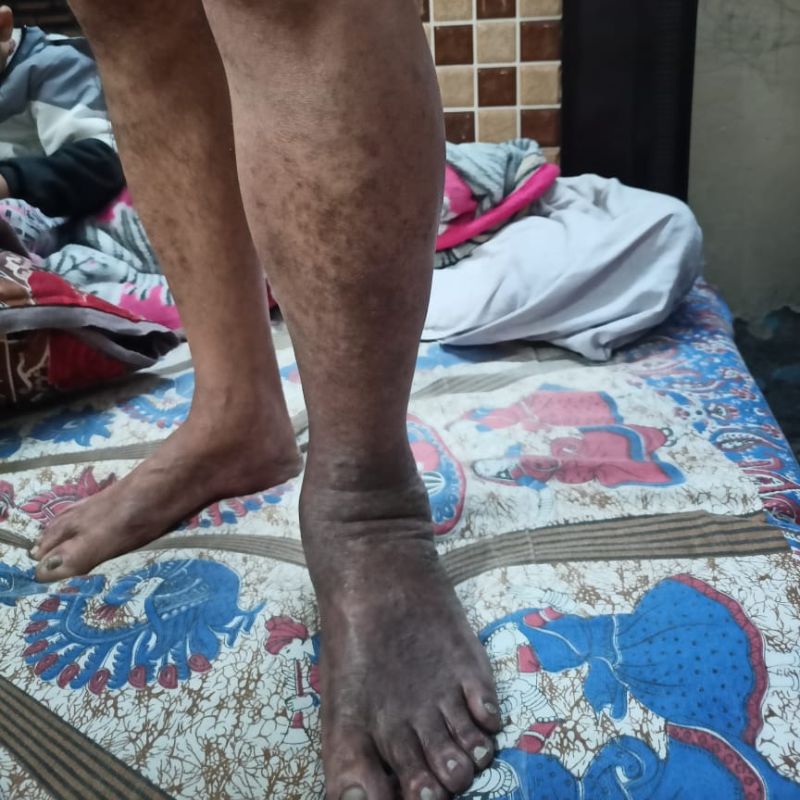
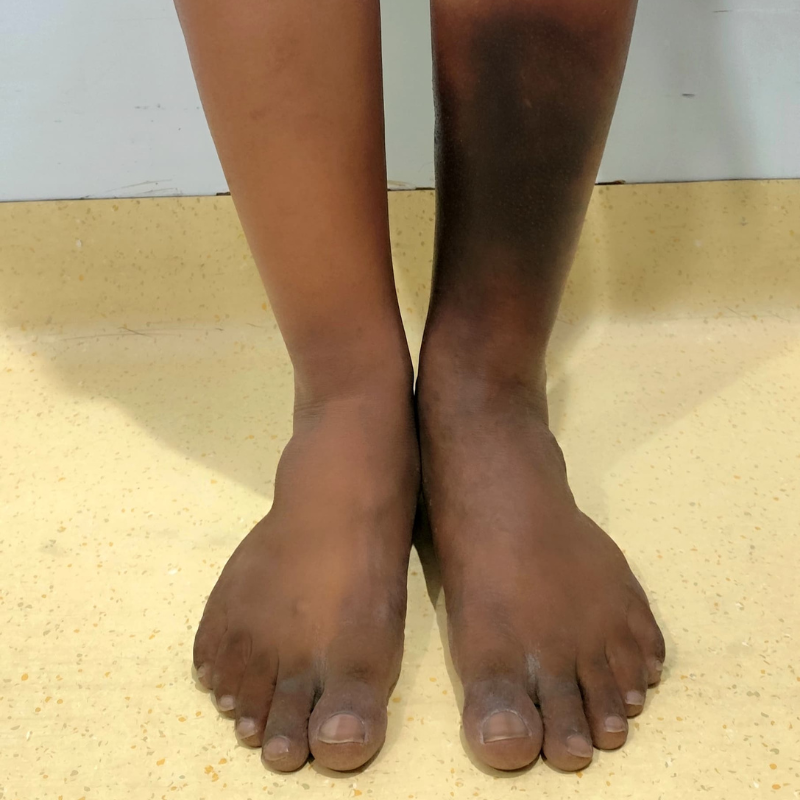

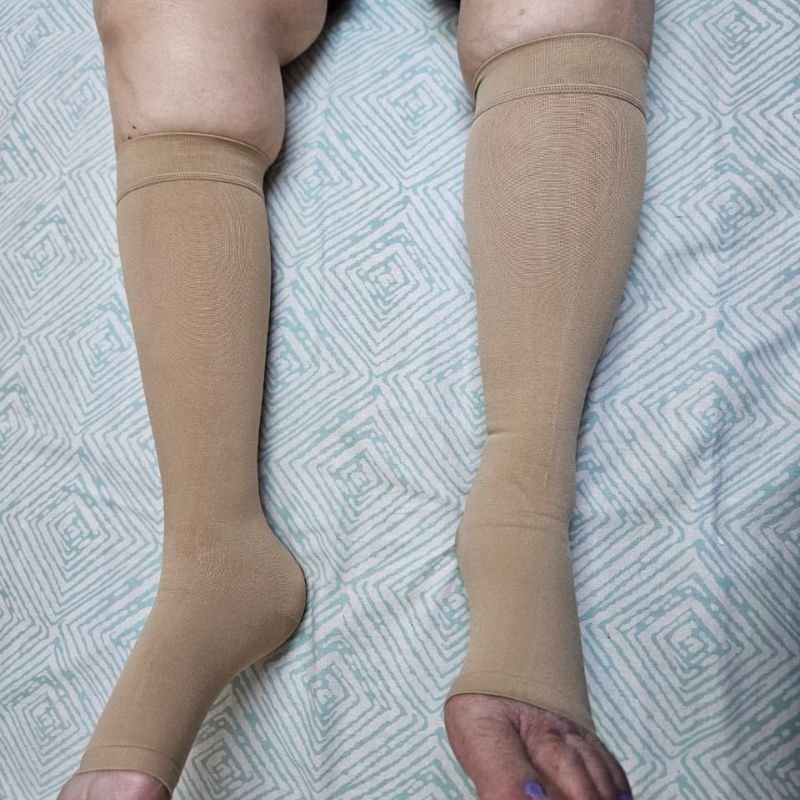
Wearing compression stockings helps:
Compression is recommended daily for several hours, especially during standing or walking. At CIIVES, we provide custom stockings to our patients based on their calf & thigh measurements.
Medications may include:
Medication cannot reverse valve damage, but it helps manage symptoms and prevent complications.
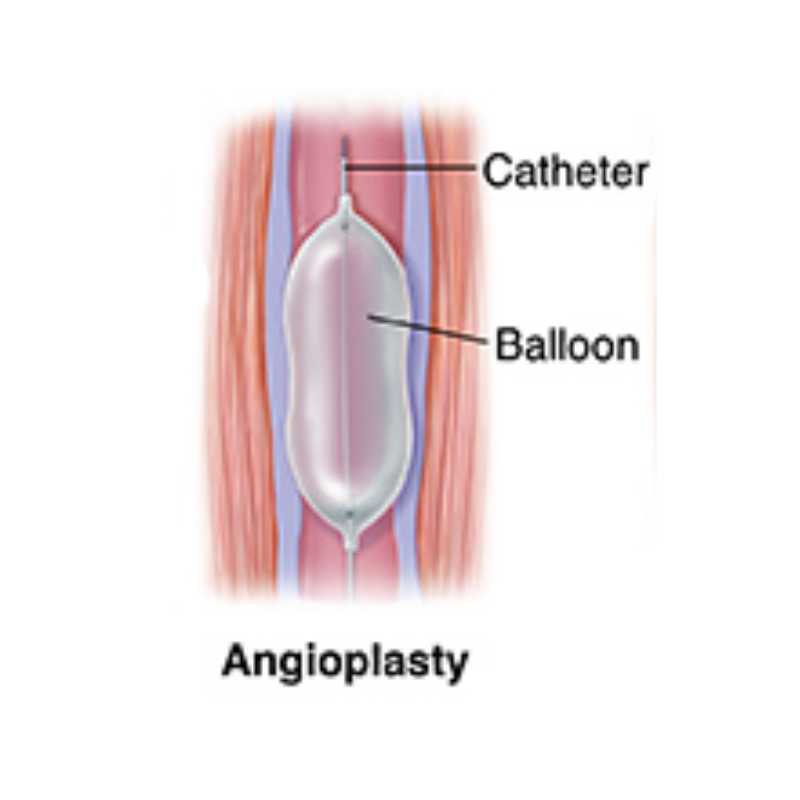
Minimally invasive procedures such as venoplasty or stenting can:
These procedures are usually considered when conservative measures are insufficient or symptoms significantly impact daily life.
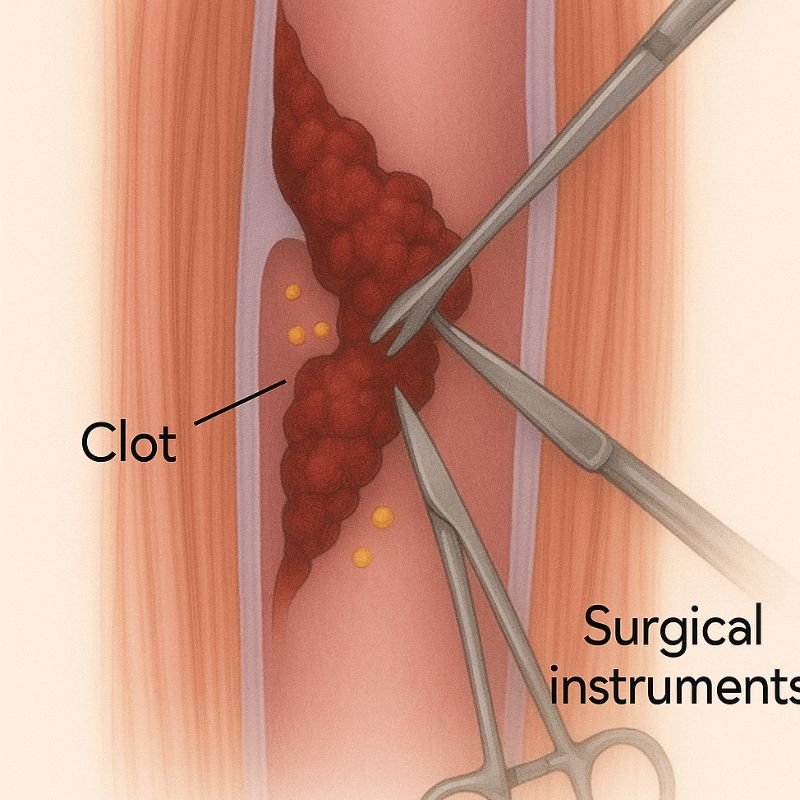
In severe or complicated cases, surgical intervention may be recommended:
Surgery is generally reserved for patients who do not respond to conservative or endovascular treatments.
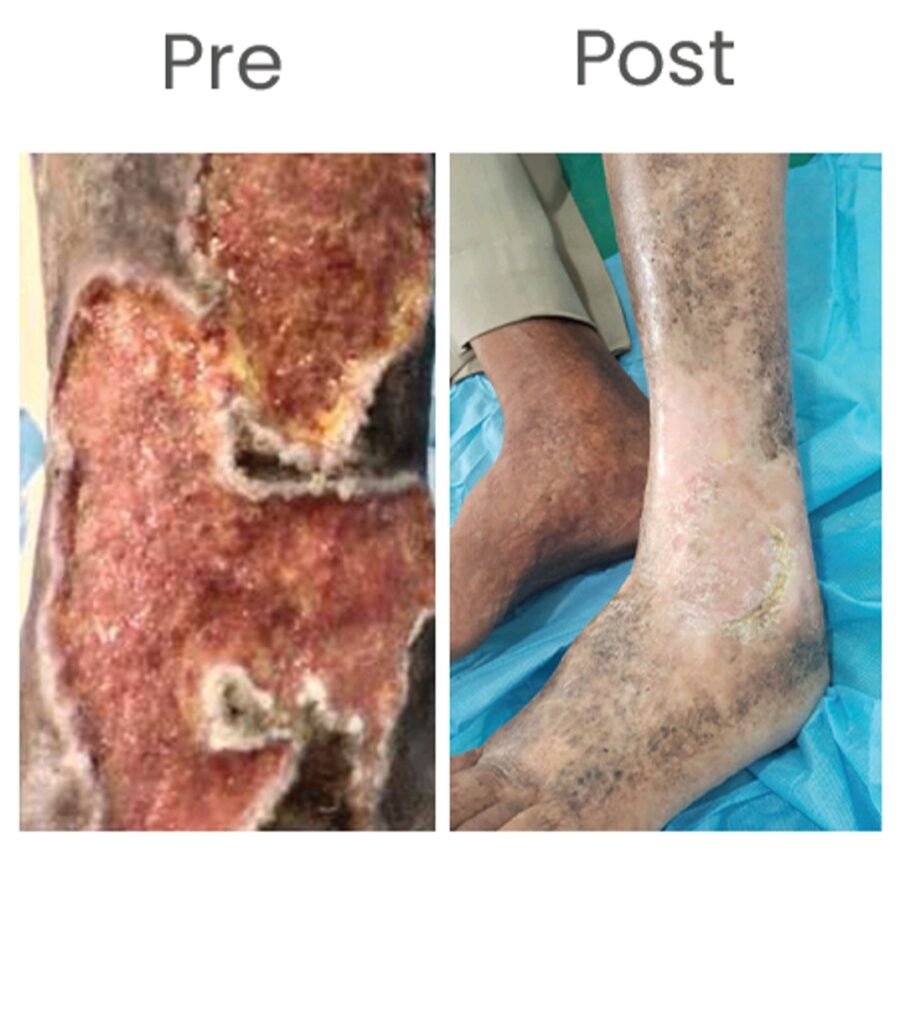
Watch expert videos explaining how PTS develops and how endovascular treatments can restore vein health.