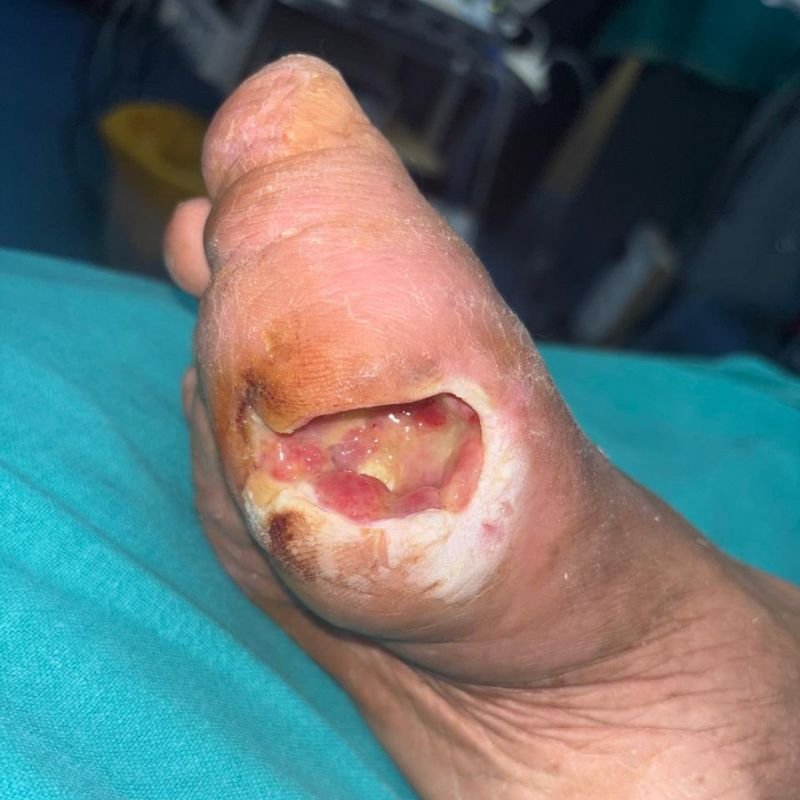
Diabetic foot refers to a range of foot problems that develop in people with long-term high blood sugar levels. Over time, diabetes damages small blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the feet.
It also causes nerve damage or peripheral neuropathy, which lowers sensation and makes it harder to feel pain, pressure, or injuries. As a result, even minor cuts & wounds go unnoticed.
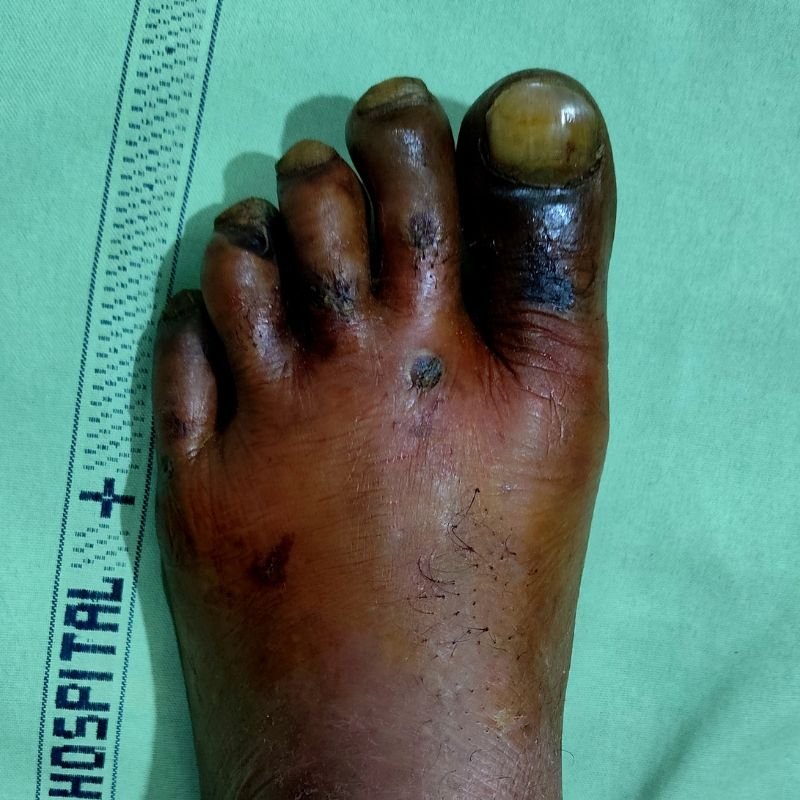
Poor circulation and high blood sugar create an environment prone to infections and impaired healing. If left untreated, these injuries can turn into non-healing ulcers and, in severe cases, lead to gangrene (black foot), where tissue dies and amputation may be necessary.
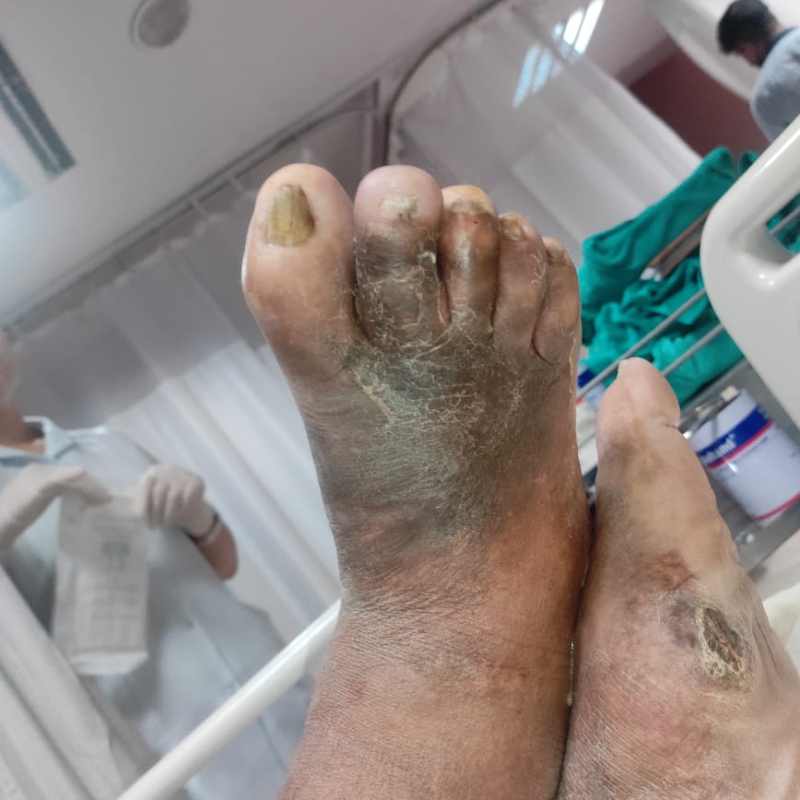
Diabetic foot problems often develop gradually due to glycation, where high blood sugar binds with fats & proteins in the bloodstream to form advanced glycation end-products (AGEs).
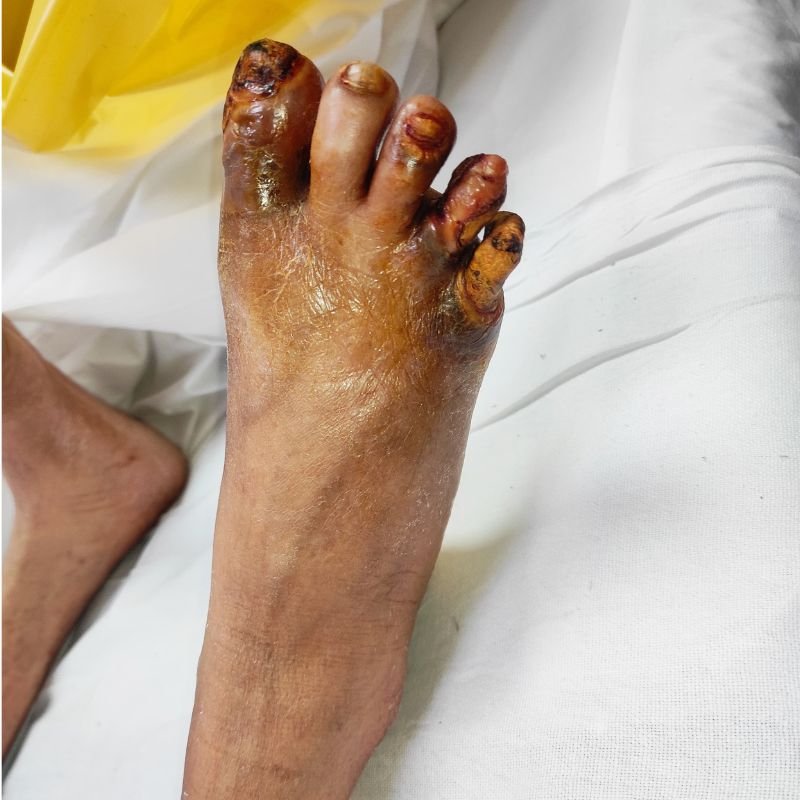

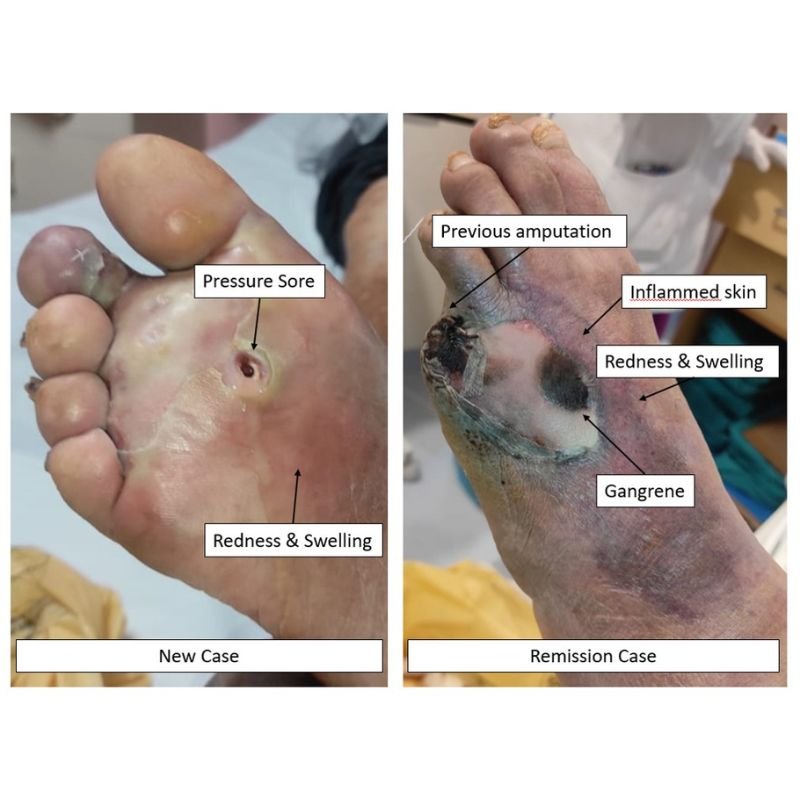
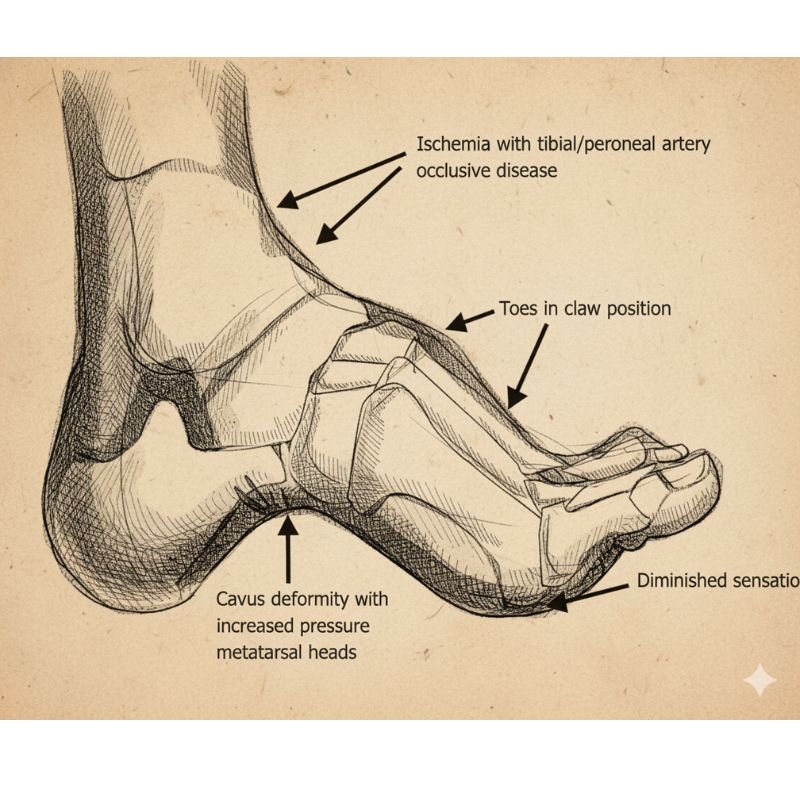

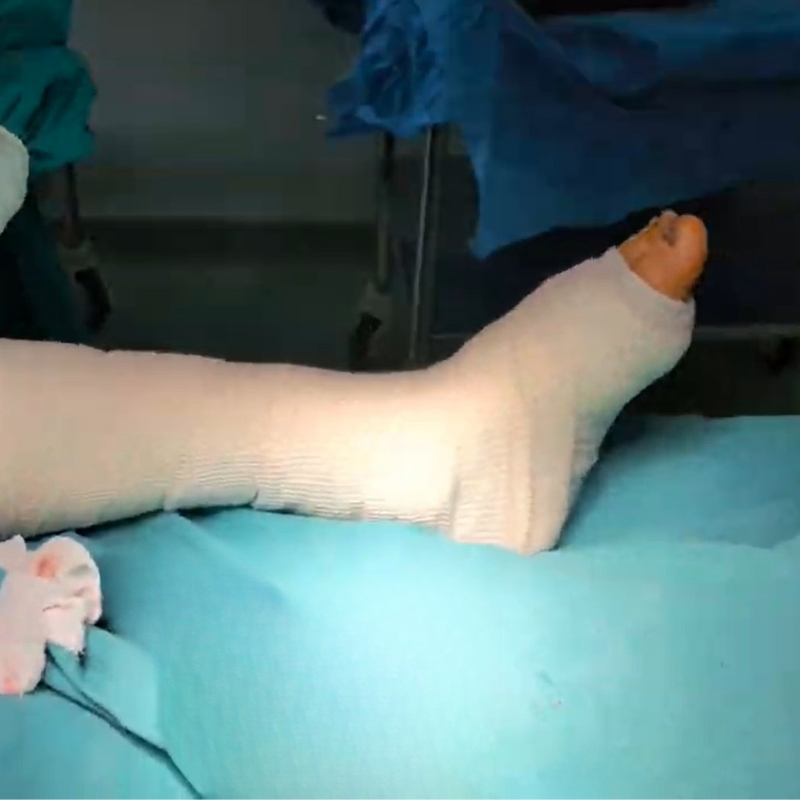
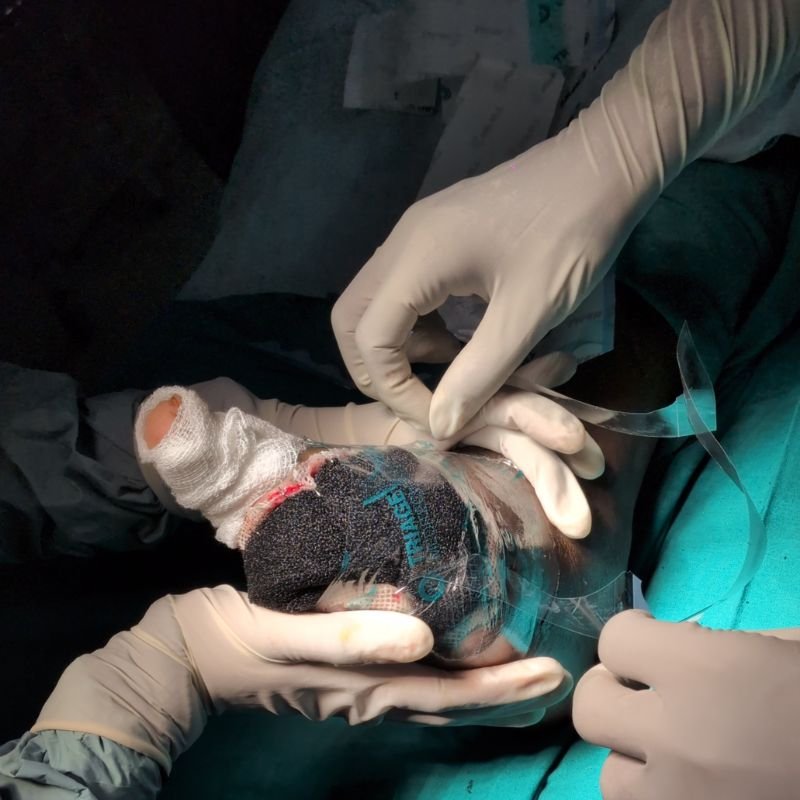
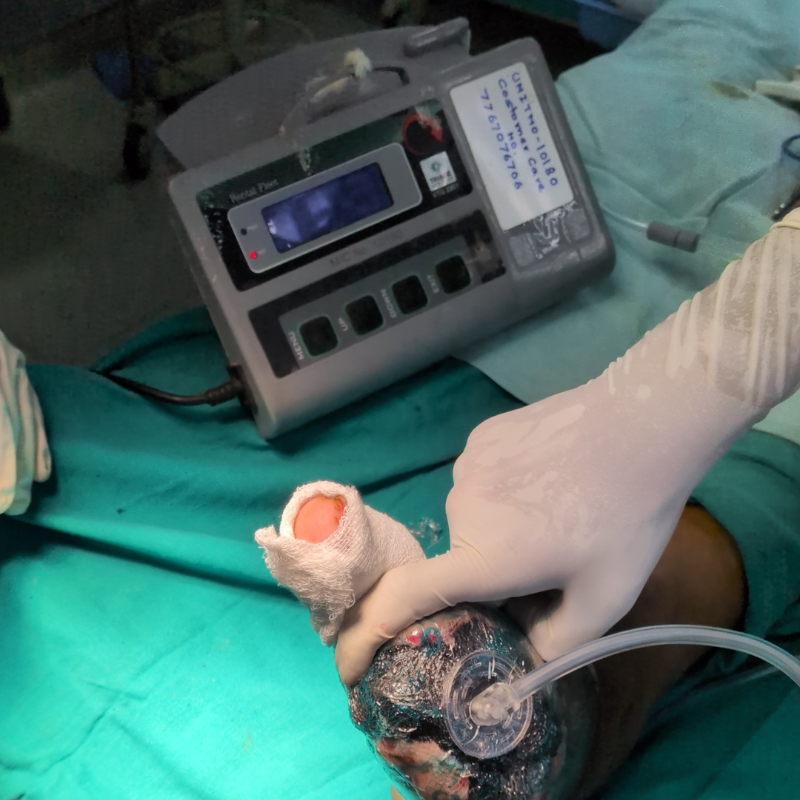
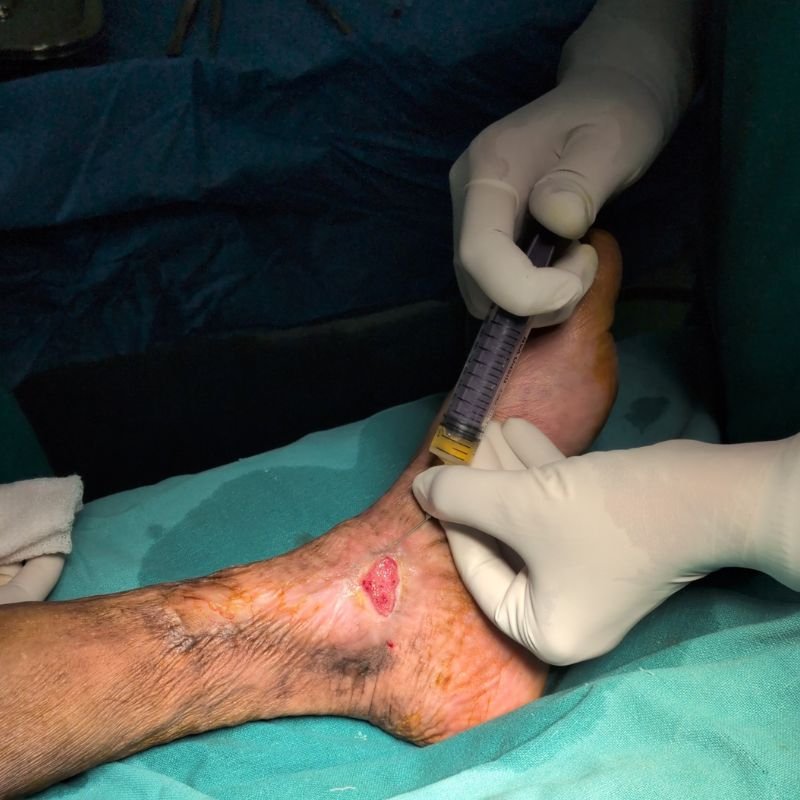
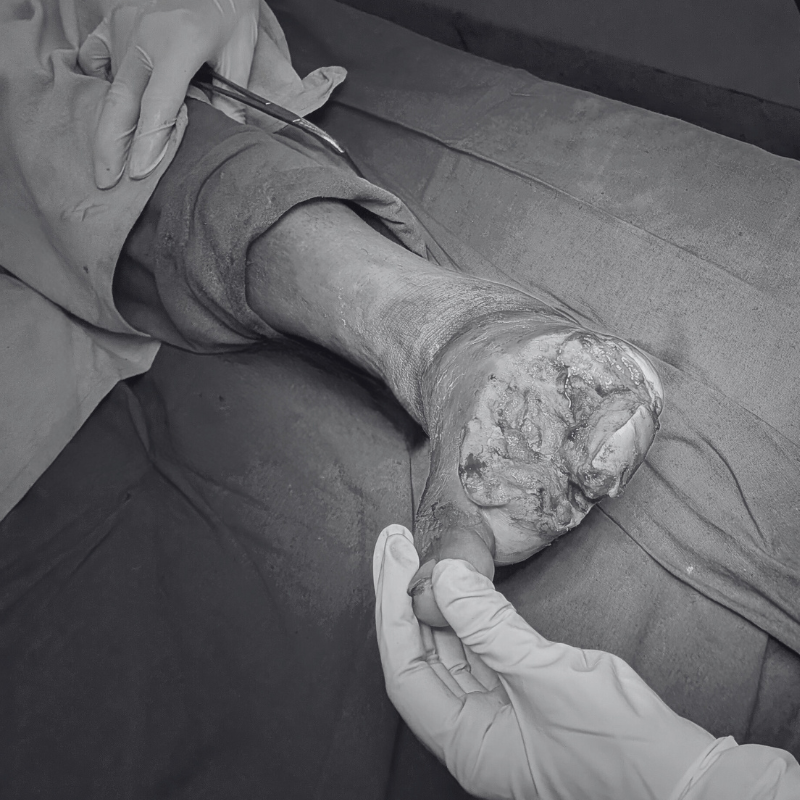
Discover how minimally invasive treatments help relieve pain and improve the appearance of legs.
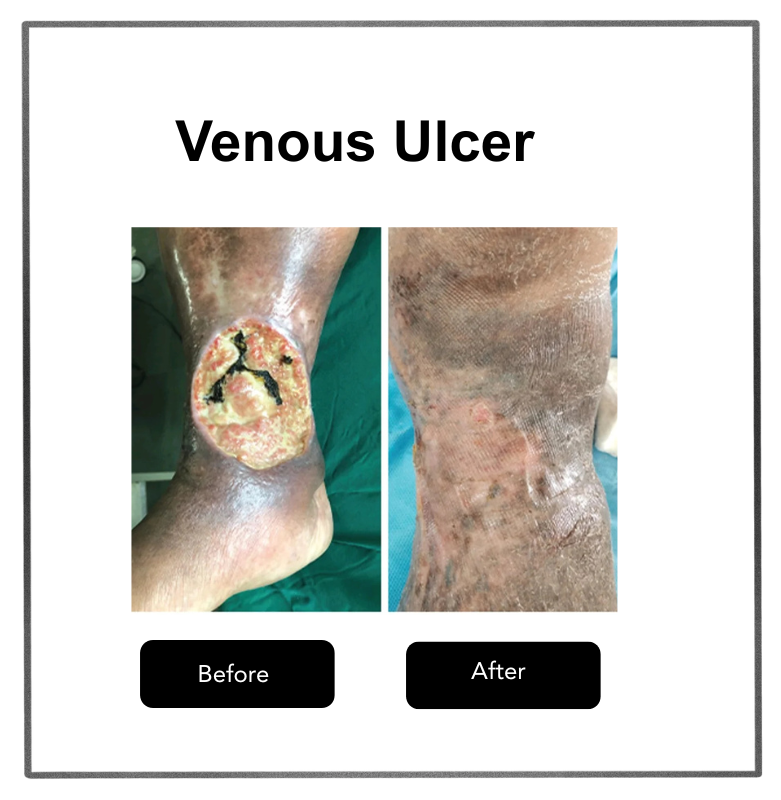
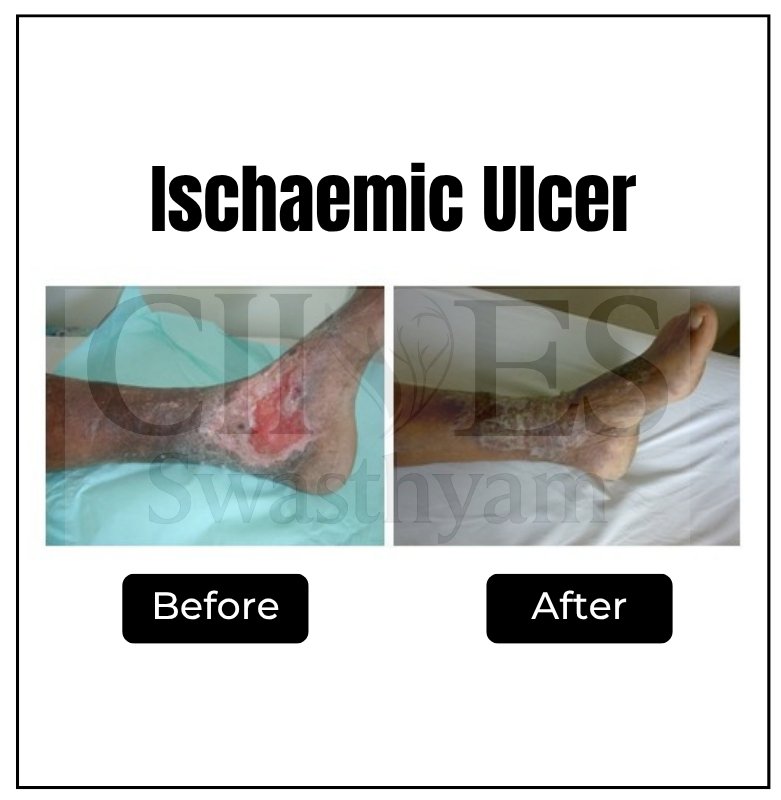
Watch expert videos to understand how diabetes affects your feet and how timely vascular intervention can prevent severe infections and amputations.
Explore related articles to know more about Varicose Vein, ways to prevent it, and how to care for yourself after treatment.
If you’re a diabetic, schedule a consultation with our team for a detailed diabetic foot assessment.